The Compound Interest Calculator Helps You Work Out:
- What Money You’ll Have If You Save a Regular Amount: Calculate the future value of regular savings contributions, showing you the potential growth of your investments over time.
- How Compounding Increases Your Savings Interest: Visualize the way compounding accelerates your savings by continuously earning interest on both your initial principal and the accumulated interest from previous periods.
- The Difference Between Saving Now and Saving Later: Understand the impact of starting your savings early versus delaying, highlighting the benefits of compounding over a longer period.
- How to Calculate Compound Interest: Provide a straightforward method to compute compound interest using the principal amount, interest rate, compounding frequency, and duration.
Compound Interest Calculator
Initial Deposit: $0.00
Total Regular Deposits: $0.00
Total Interest: $0.00
Total Savings: $0.00
Understanding Compound Interest
Compound interest, often hailed as one of the most powerful financial concepts, is the interest calculated on the initial principal, which also includes all of the accumulated interest from previous periods. It can dramatically increase savings and investments over time, making it a key tool for financial growth, especially in Australia, where savvy investment strategies are highly valued.
What is Compounding?
Compounding refers to the process where the value of an investment increases because the earnings on an investment, both capital gains and interest, earn interest as time passes. This effect can cause wealth to grow exponentially over time, making it a crucial concept for personal financial planning.
Compounding Interest Calculator Australia
Our compound interest calculator is a tool designed to help you project the growth of your investments under the parameters of compound interest. Here’s how you can use this tool effectively:
- Initial Deposit: Enter the starting amount of your investment. This is your principal amount on which interest will compound.
- Regular Deposit: Input the amount you plan to add to your investment regularly. This could be monthly, quarterly, or annually.
- Annual Interest Rate: Specify the interest rate. Ensure it's the annual rate and not a monthly or quarterly rate.
- Compound Frequency: Choose how often you want the interest to be compounded—annually, semi-annually, or monthly.
- Number of Years: Decide the duration for which you want to stay invested or the period over which you wish to calculate compound interest.
Once you input these details, hit "Calculate" to see how much your investment will grow over the years.
How do you calculate compound interest
The formula used for calculating compound interest is:
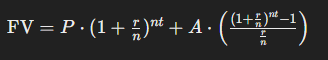
Where:
- FV = Future Value
- P = Principal amount (Initial Deposit)
- r = Annual Interest Rate
- n = Number of times interest is compounded per year
- t = Number of years
- A = Regular deposit amount
This compound interest formula is crucial for calculating detailed future savings, especially when using tools like a monthly compound interest calculator.
Compound Interest in Action
Compound interest has a remarkable ability to amplify savings and investments over time. Let's explore some real-life examples that showcase the power of compound interest in action:
- Retirement Planning: Imagine you start investing $200 per month in a retirement account at age 25, with an average annual return of 7%. By the time you reach 65, your investment could potentially grow to over $500,000. This substantial growth is mainly attributed to the compounding effect, where your earnings generate additional earnings over decades of consistent contributions.
- Education Savings: Suppose you open a college savings account for your child's education with an initial deposit of $5,000 and contribute $100 per month. With an average annual return of 5%, the account could grow to more than $30,000 by the time your child turns 18. This demonstrates how starting early and leveraging compound interest can alleviate the financial burden of higher education expenses.
- Debt Repayment: On the flip side, compound interest can also work against you when dealing with debt. Consider a credit card balance of $5,000 with an annual interest rate of 18%. If you only make the minimum monthly payment, it could take over 20 years to pay off the debt, and you would end up paying more than $8,000 in interest alone. This highlights the importance of prioritizing debt repayment and avoiding high-interest loans whenever possible.
- Investment Diversification: Diversifying your investment portfolio is another effective strategy to maximize compound interest returns. By spreading your investments across various asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, and real estate, you can mitigate risk and capitalize on different growth opportunities. Over time, the compounding effect of these diverse investments can lead to significant wealth accumulation and financial security.
These examples illustrate the profound impact of compound interest on financial outcomes. Whether you're saving for retirement, funding your children's education, or managing debt, understanding and harnessing the power of compound interest can help you achieve your long-term financial goals with confidence.
Harnessing the Power of Compound Interest
Compound interest is not merely a financial concept; it's a dynamic force that can shape the trajectory of your financial journey. As we conclude our exploration of compound interest, let's reflect on its significance and practical implications:
- Long-Term Wealth Building: At its core, compound interest is a wealth-building tool that rewards consistency, patience, and strategic planning. By reinvesting your earnings and allowing them to compound over time, you can unlock the potential for exponential growth in your savings and investments.
- Strategic Financial Planning: Understanding compound interest empowers you to make informed decisions about savings, investments, and debt management. Whether you're setting aside funds for retirement, funding major expenses, or paying off loans, incorporating compound interest calculations into your financial strategy can optimize your outcomes and accelerate your progress towards financial independence.
- Leveraging Technology: In today's digital age, access to compound interest calculators and financial planning tools has never been easier. Take advantage of online resources and mobile applications to simulate various scenarios, analyze potential outcomes, and fine-tune your financial goals. By harnessing the power of technology, you can gain valuable insights into your financial future and make proactive decisions to optimize your wealth accumulation.
- Continuous Learning and Adaptation: The financial landscape is constantly evolving, presenting new opportunities and challenges along the way. Embrace a mindset of continuous learning and adaptation, staying informed about market trends, regulatory changes, and emerging investment strategies. By remaining vigilant and adaptable, you can navigate financial uncertainties with confidence and resilience, maximizing your potential for long-term success.
- Community and Collaboration: Finally, remember that you're not alone on your financial journey. Seek guidance from trusted advisors, engage with like-minded peers, and leverage community resources to support your growth and learning. By collaborating with others and sharing insights and experiences, you can enrich your financial knowledge, expand your network, and enhance your overall financial well-being.
Conclusion
Understanding and utilizing compound interest is essential for anyone looking to grow their savings or investments. Whether you're calculating compound interest in Australia, using CBA’s tools, or setting up compounding in Excel, the fundamental principles remain the same and can significantly impact your financial planning. Equip yourself with a robust compound interest calculator to see how your investments could potentially expand over the years.
FAQs About Compound Interest
What is the meaning of compound interest?
Compound interest is the calculation of interest on the initial principal, which also includes all of the accumulated interest from previous periods. It's what allows investments to grow at an exponential rate over time.
How do you calculate compound interest?
You can calculate compound interest using the formula mentioned above or by using a compound interest calculator, which simplifies the process.
How do you compound monthly?
To compound monthly, set the compounding frequency in the formula to 12. This means interest is calculated and added to the principal every month.
How to calculate the interest rate?
To find the interest rate when other variables are known, rearrange the compound interest formula to solve for r.
How do you calculate interest per year?
Annual interest can be calculated by setting the compounding frequency to 1 in the compound interest formula, ensuring the calculation is done once per year.
How to do compounding in Excel?
Use the FV function in Excel, which stands for "Future Value." The syntax can be as follows: =FV(rate, nper, pmt, [pv], [type]), where rate is the interest rate per period, nper is the total number of payment periods, pmt is the payment made each period, and pv is the present value.
What are the 3 types of compound interest?
Daily Compounding: Interest is calculated and added to the principal daily.
Monthly Compounding: Interest is calculated and added monthly.
Annually Compounding: Interest is added once per year.
What is compound interest?
Compound interest is the interest calculated on the initial principal and also on the accumulated interest of previous periods. It's a powerful concept in finance where your money grows exponentially over time. This growth is often expressed using the compound interest formula.
How much is $1000 worth at the end of 2 years if the interest rate of 6% is compounded daily?
To calculate the future value, we use the compound interest formula: FV = P(1 + r/n)^(nt), where FV is the future value, P is the principal amount, r is the annual interest rate (as a decimal), n is the number of times interest is compounded per year, and t is the time in years. For $1000 at 6% compounded daily for 2 years: FV = 1000(1 + 0.06/365)^(365*2).
Is compound interest good or bad, and why?
Compound interest is generally considered good because it allows investments to grow over time, increasing wealth. It's a key factor in accumulating savings and achieving long-term financial goals, such as retirement planning or building wealth.
How is compound interest calculated?
Compound interest is calculated using the formula: FV = P(1 + r/n)^(nt), where FV is the future value, P is the principal amount, r is the annual interest rate (as a decimal), n is the number of times interest is compounded per year, and t is the time in years.
How long will it take $4000 to grow to $9000 if it is invested at 7% compounded monthly?
Using the compound interest formula, we can calculate the time required. Rearranging the formula to solve for t: t = ln(FV/P) / (n * ln(1 + r/n)). For $4000 to grow to $9000 at 7% compounded monthly: t = ln(9000/4000) / (12 * ln(1 + 0.07/12)).
How much will $10,000 be worth in 20 years?
To find the future value, use the compound interest formula: FV = P(1 + r/n)^(nt). For $10,000 at a certain interest rate compounded over 20 years.
How much can I earn with a $10,000 CD?
The earnings from a Certificate of Deposit (CD) depend on the interest rate and term length. Use the compound interest formula to calculate the future value of the CD investment.
How to start earning compound interest?
You can start earning compound interest by investing your money in interest-bearing accounts, such as savings accounts, CDs, or investment accounts. Regular contributions and reinvestment of earned interest can accelerate the growth of your investments.
What will 1 million be worth in 30 years?
Use the compound interest formula to calculate the future value of $1 million invested at a certain interest rate compounded over 30 years.
Expand Your Financial Knowledge: Visit our Personal Finance section for essential tips, delve into Property Investing for the latest market insights, or explore our comprehensive Resources for educational articles and tools. If you’re interested in the stock market, our Shares & ETFs section offers a range of options to suit your investment goals. Dive into these areas to enhance your financial understanding and decision-making.
Disclaimer
Estimations for Illustrative Purposes: The GST calculations generated by this Australian GST Calculator are approximations intended for educational and illustrative purposes only. While we strive for accuracy, actual GST liabilities may differ due to specific circumstances or changes in tax laws.
Excludes Other Considerations: This Australian GST Calculator focuses solely on Goods and Services Tax (GST) estimations. It does not incorporate other potential fiscal obligations, such as additional taxes, levies, or deductions that may impact the total amount payable when managing your finances or business operations.
Not Professional Financial Advice: The use of this GST calculator does not constitute financial advice. It is not intended to replace professional consultation and should not be the only factor in making financial decisions. For personalized financial guidance, we recommend seeking advice from a qualified tax consultant or financial advisor.
Use at Your Discretion: By using this Australian GST Calculator, you understand and agree that the outcomes are estimates and that your specific tax situation may vary. Any actions taken based on the calculator’s results are done at your own discretion and risk.
Not a Licensed Financial Advisor
The information and insights provided in this document are intended solely for educational and informational purposes. It’s imperative to understand that I am not a licensed financial advisor, tax expert, or investment strategist. The contents herein are crafted to offer a general overview and should not be construed as personalized financial advice.
Affiliate Disclosure: Some of the links on this blog may be affiliate links. This means if you click on the link and purchase a product or service, I may receive a commission at no additional cost to you. I only recommend products or services that I believe in, and that may be helpful to my readers.
Before making any financial decisions or embarking on investment ventures, it’s crucial to consult with a professional financial advisor or a certified tax consultant who is well-equipped to understand your unique financial landscape. Engaging with a licensed professional ensures that the advice you receive is tailored to your specific financial goals, risk tolerance, and tax obligations, adhering to the compliance and guidelines established by regulatory authorities, including the Australian Taxation Office (ATO) and other relevant bodies.
Financial markets are complex and dynamic and involve various degrees of risk. Therefore, thorough due diligence and professional guidance are essential to navigate these waters effectively. This content does not represent the opinions or endorsements of any financial institutions or regulatory agencies. Remember, the responsibility for financial decisions lies with the individual, and seeking qualified advice is the best step towards informed decision-making and achieving financial objectives.
